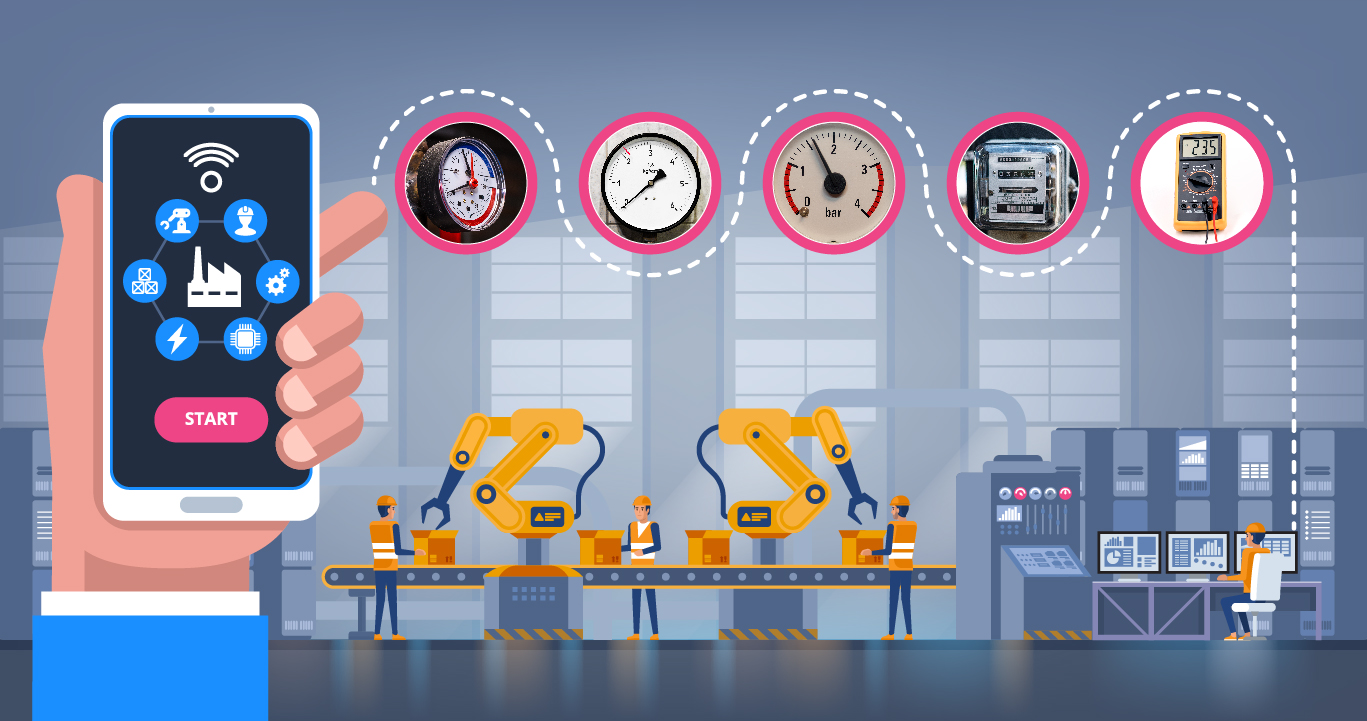
Utilities contribute significantly to the recurring expenses in a factory, but often are not used properly. Utility controllers can be used to detect usage, and using IoT, they can help factories not only make huge savings on expenses but also predict any equipment malfunctions.
Utility controllers are generally based on sensors. Micro-Electro-Mechanical System (MEMS)-based sensors have come a long way since their invention and first use in the mid-twentieth century to evolve into the Nano-Electro-Mechanical System (NEMS)-based sensors of today. Besides, event-driven and time-driven controllers also play an important role.
Utility Controllers
HVAC usage controllers

Pressure sensors on the doors and windows can detect the open condition of doors along with the time and location, leading to reduced efficiency of the HVAC equipment and spiralling energy bills.
Humidity sensors and Air Quality sensors help in proper usage of existing HVAC equipment to the optimum temperature. In the electronics industry, they help reduce obnoxious fumes from soldering machines and flux. These sensors help maintain employee well-being.
Air repair mechanic using measuring equipment for filling industrial factory air conditioners and checking maintenance outdoor air compressor unit.
Water usage controllers

Motion detection controllers are used in automated sinks, faucets, toilet flushers and hand dryers to minimise water wastage.
Water Quality sensors ensure appropriate use of water for consumption or other activities.
Current usage controllers
Idling equipment need to be switched off to ensure reduced power bills. Current monitoring sensors can also indicate malfunctioning equipment for appropriate action.
Access Controllers
Access to factory premises is controlled by access controllers. Within the factory too, only restricted people are allowed in certain zones requiring RFID-based or similar entry.
IR Sensing controllers
These are the most common types of sensors which find use in a variety of applications such as remote controls, breath analysis, infrared vision to visualise heat leaks in electronics and non-contact-based temperature measurements. They are of high utility value to many IoT projects in the healthcare industry.
Smoke and Fire Detection controllers

3d rendering smoke detector on ceiling
Smoke detectors within a work area can warn of potential malfunctioning of any equipment or impending danger in the form of fire incidence. Fire detectors perform a similar role, thwarting any fire hazard from happening.
Imaging and Optical sensors
Image sensors find their use in multiple ways. They are implemented to improve security systems in the premises and to control access.
Robotic Sensors
More and more factories today are using robotics. The robots and cobots use many sensors such as gyroscope sensors, accelerometer sensors, collision detection sensors and the associated End of Arm Tooling (EOAT) uses various pressure and magnetic sensors. These sensors ensure proper functioning of robotics.
Other sensors
Besides, industry-specific sensors are used in specialised industries such as liquid processing, petrochemical and mining.
Event-driven and time-driven controllers
Many controllers are activated at specific times of the day triggering, for example, lights to be turned on after 6PM and turned off after 6AM, thus saving on energy consumption.
Some events trigger the activation of controls to perform specific tasks, for example, in the event of an untoward power fluctuation the equipment is turned off automatically, protecting it from being damaged and avoiding the repair costs.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), Cobots and moving utility vehicles stop when they near any obstruction in the form of material or humans in a collaborative environment.
Smart Controllers
All the above types of controllers detect variation in other forms of energy and share the information in digital signals. This information is captured in real-time by data loggers and presented in a meaningful format which is used for appropriate decisions. IoT based gateway-less communication between equipment or through the cloud result in better planning and production.
Profitability of a factory is improved by reducing wastage on unused resources. Many direct benefits accrue such as the performance analysis of equipment. When an equipment is found to generate more heat or is vibrating more than is normal, it may be an indication of machine wear and tear and calls for maintenance. Many faults are detected by these sensors in real-time, much ahead of any potential damage to equipment leading to costly repairs on equipment in addition to easily avoidable downtime. Many hidden defects are detected which can be potentially hazardous to employee well-being, such as water and air quality.
Overall Equipment Efficiency (OEE) can be improved by analysing the different manufacturing/processing lines within a factory, e.g. the body shop is producing the desired results but the paint shop calls for closer scrutiny of the paint shop or any specific equipment within it. Similarly, for a factory in multiple locations, any non-performing equipment in a location may be moved to another where it can be better utilised.
The analysis of information over a period of time helps factories to plan into the future for better productivity, quality and profitability.
The Industrial IoT Solutions India from MELSS offers comprehensive IoT solutions including hardware, firmware and software. We deliver solutions for both on-premise and cloud based implementation. For more: https://www.melss.com/latest/industry-4-0/